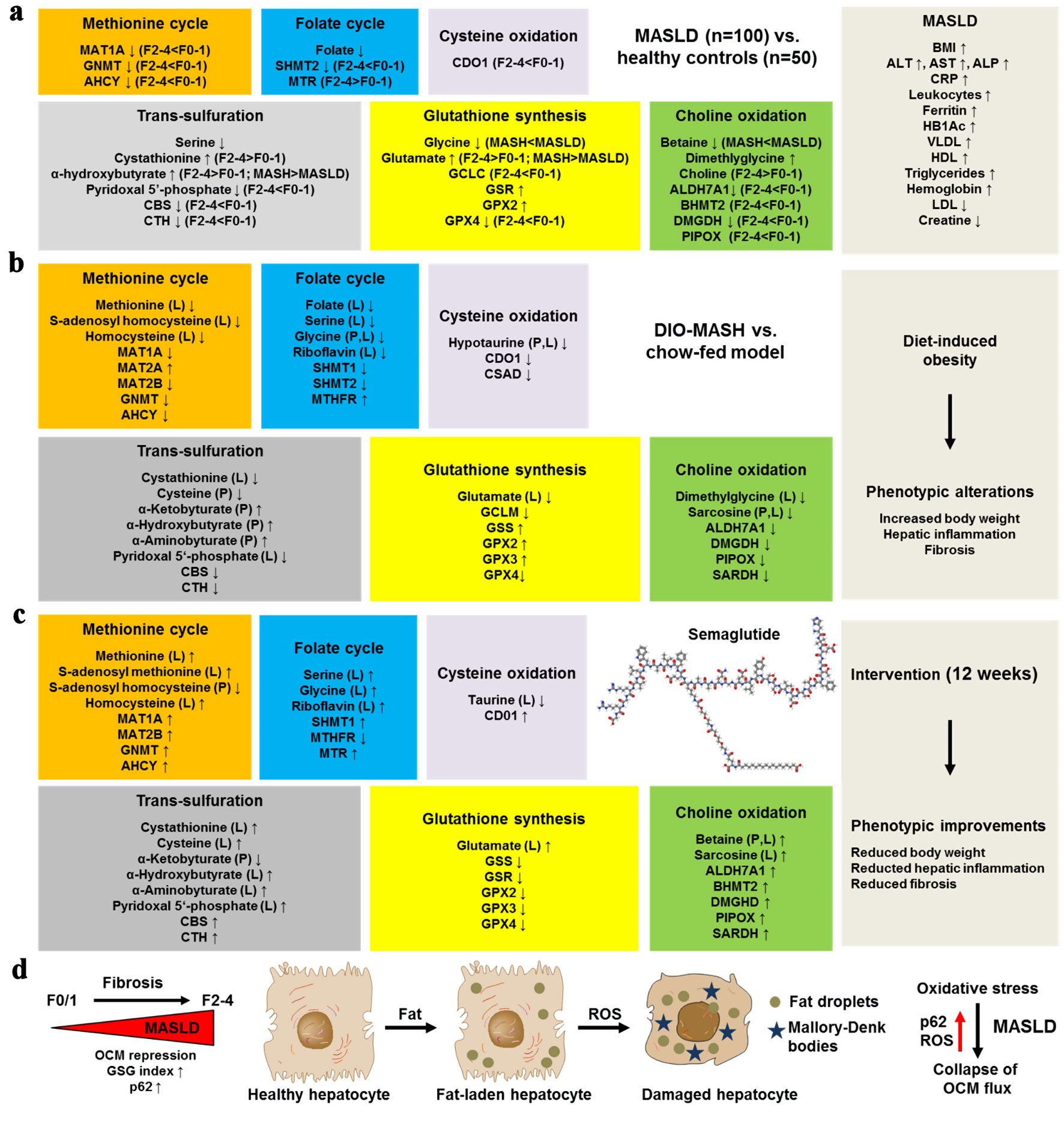
Figure 1. Semaglutide rebalances one-carbon metabolism (OCM) along the progression of MASLD. (a) Metabolic alterations occur in the methionine cycle, folate cycle, cysteine oxidation, choline oxidation, transsulfuration, glutathione synthesis, and choline oxidation pathways in human MASLD. This was observed in 100 biopsy-proven MASLD patients versus 50 healthy controls. (b) Similar metabolite and transcriptional changes occur in the mouse DIO-MASH model as in human MASLD. (d) In the mouse DIO-MASH model, semaglutide intervention for 12 weeks led to the normalization or “over-correction” of key metabolites. (d) MASLD and ongoing fibrosis are further associated with increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and increased expression of the sequestosome protein p62 in fat-laden, ballooned hepatocytes, which drive the collapse of OCM flux. AHCY: adenosylhomocysteinase; ALDH7A1: aldehyde dehydrogenase 7 family member A1; ALP: alkaline phosphatase; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; BHMT2: betaine-homocysteine S-methyltransferase 2; BMI: body mass index; CBS: cystathionine beta synthase; CDO1: cysteine dioxygenase; CRP: C-reactive protein; CSAD: cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase; CTH: Cystathionine γ-lyase; DIO: diet-induced obesity; DMGDH: dimethylglycine dehydrogenase; GCLC: glutamate-cysteine ligase C; GCLM: glutamate-cysteine ligase M; GNMT: glycine N-methyltransferase; GPX2: glutathione peroxidase 2; GPX4: glutathione peroxidase 4; GSS: glutathione synthetase; GSR: glutathione-disulfide reductase; Hb1Ac: glycated hemoglobin; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; MAT1A/2A/2B: methionine adenosyltransferase 1A/2A/2B; MTHFR: methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase; MTR: methionine synthase; PIPOX: pipecolic acid and sarcosine oxidase; SARDH: sarcosine dehydrogenase; SHMT1/2: serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1/2; VLDL: very-low-density lipoprotein.